There is growing evidence that teaching executive functioning skills in the classroom can positively impact students’ academic performance. It’s the driving force helping students to complete tasks, remember information, and regulate their behavior.
Unfortunately, many teachers are not teaching these skills directly. They assume students will develop them independently, or that they are unimportant. The reality, however, is that executive functioning skills are essential for academic success. But what’s the concept behind this term, and why do researchers believe teaching these skills in school is so important?
Scientific Perspectives
Executive function (EF) is an umbrella term for a neuroscientific phenomenon describing the neurological processes involving cognitive control and self-regulation. The executive of the brain is located in the prefrontal cortex, which is the brain’s frontal lobe. In other words, it’s the driving force helping us to complete tasks, remember information, and control our impulses.
The term has a deeper interpretation, underscoring the unique ability to consciously control our thoughts, actions and emotions. People activate executive functioning skills whenever they need to break away from undesirable habits or plan something.
Executive function has many expressions, like time management, working memory, inhibitory control, and task flexibility. All of which fall under the general concept of self-regulation.
However, teaching executive functioning skills is particularly important in the classroom.
Teaching Executive Functioning Skills in the Classroom
Each student is unique in their mental and physical abilities. Children with ADHD, for example, tend to have weaker skills. This can present itself in disruptive behavior or a general inability to focus on tasks. Teachers who underestimate the role of EF often end up reprimanding their students for forgotten homework, lateness, or poor test grades.
Students with well-developed executive functions thrive in school and build a solid foundation for success in life. While teachers should always set rules and expectations in the classroom, they also need to understand that some students have difficulties following them. When teachers take the time to teach the relevant competencies, they give their students the tools they need to succeed.
So, what’s your role as a teacher? There are many things that can be done to support the development of these vital skills in your students. Let’s look at several strategies and activities you can start implementing today!
Tips to Improve Executive Functioning Skills in Students
EF relies on three types of brain functions:
- Working memory – responsible for retaining and manipulating information at a given moment
- Mental flexibility – responsible for sustaining or shifting attention from one thing to another
- Self-control – responsible for maintaining focus, keeping track of what’s important and ignoring distractions
Each of these functions is supported by different teaching strategies.
Activities to Improve Working Memory
This skill is essential for learning new information and retaining it in the short term. Here are several teaching strategies teachers can use to support working memory development in their students.
Use Mnemonic Devices
These memory tools help students associate new information with something they already know. A classic example is the acronym “ROY G. BIV,” used to remember the rainbow colors – red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet.
Make Connections
When teaching a new lesson, connect it to something your students already know. When students use mental imagery, they create a picture in their minds to remember some things. Inserting those images into a child’s mind will develop their working memory skills. Concept maps and visually appealing graphics can also help.
Use digital collaborative whiteboards to visualize new concepts and explain the connections between two or more ideas. Some teachers prefer breaking down information into manageable “chunks.” Here’s how one teacher explained the main tourist attractions across Europe, gathering together the main points on a digital whiteboard.
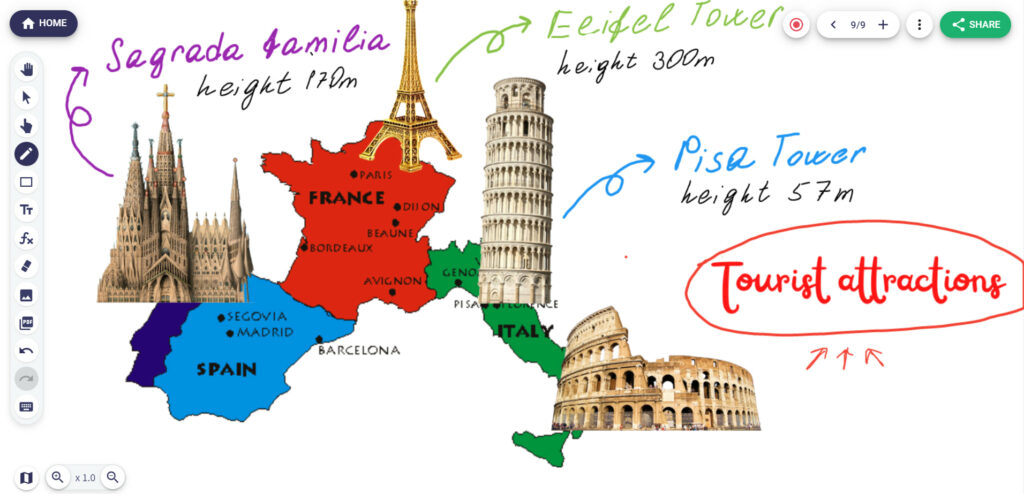
Don’t Forget About Yourself
Since working memory is essential for teaching, ensure your brain is in peak condition. Take care of yourself by eating healthy, sleeping well and exercising regularly. Also, keep your teaching materials organized and easy to access to avoid stressful situations.
It’s more challenging to keep track of what’s happening around you when you’re fatigued. This can lead to forgetfulness and decreased productivity.
Activities to Improve Mental Flexibility
This skill is about attentiveness and the ability to switch focus when necessary. Here are some teaching strategies you can use to support mental flexibility development in your students.
Encourage Questions
Asking questions means students are actively engaging with the lesson material. Ask questions in class around the teaching material to motivate students to pay attention and think critically about the topics you’re discussing. Also encourage them to ask questions about the parts they don’t understand.
Optimize Digital Tools
Incorporating technology in the classroom can help students develop mental flexibility and comprehend new concepts quickly. Using digital boards synched with laptops and tablets will make students remain constantly attentive.
For example, add interactive quizzes to your technologically enhanced classes to test students’ progress with the new material.
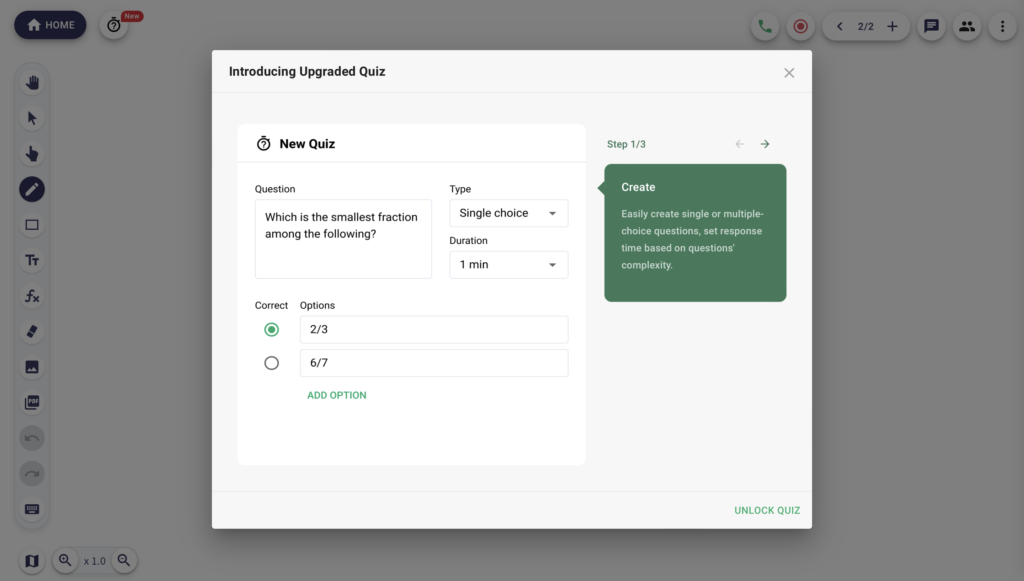
This strategy can also help them learn how to multitask effectively.
Create Movement Breaks
Giving students a few minutes to move around and stretch their bodies will help them refocus and pay attention in class. Walking around or doing simple exercises will also increase the blood flow to their brains and help them stay alert.
Activities to Improve Self-Control
This function is responsible for impulse control and the ability to resist distractions. Use the following tips to teach your students the basics and importance of self-control.
Model the Skills
As a teacher, you are expected to be a role model for your students. Show them how to stay calm and focused while facing challenges. Projecting good planning and organization skills means students will be more likely to develop similar habits themselves.
Create a Classroom Routine
Habits and positive routines help students feel comfortable and safe in their learning environment. A predictable classroom routine will help them know what to expect and stay on track with their learning.
Encourage Positive Self-Talk
Teach your students to motivate themselves with positive language. When they make a mistake, encourage them to see it as an opportunity to learn and grow. Help your students develop a growth mindset by teaching them the power of effort and perseverance.
Executive functioning skills are important for success in life. They allow people to regulate their thoughts and emotions, focus on tasks, remember details, and make decisions. People with poor executive functioning skills often struggle in school and the workplace. Fortunately, there are strategies teachers can employ to help students improve these skills. Today, we’ve covered several scientific perspectives on executive functioning skills, as well as tips and activities teachers can use in the classroom to help students improve their own skills.
What’s your secret weapon in teaching executive functioning skills? Share your expertise via support@liveboard.online to help other teachers understand the matter!


